Schedule I is not just another survival or simulation game—it is a raw experiment in risk, consequence, and underground economics. At its heart lies the mechanic of drug mixing, a system that demands not only quick reflexes but also long-term strategy, resource balancing, and psychological risk management. Many new players approach it with brute force, throwing ingredients together and hoping for profitable results. Yet the real mastery comes from learning how to structure every decision, from sourcing your base substances to testing, branding, and distributing.
This guide takes you step by step through the full lifecycle of drug mixing in Schedule I. Rather than staying general, we’ll dive into detailed “how-to” instructions that build from beginner-friendly steps to expert-level optimization. If you’ve ever felt overwhelmed by the complexity of combinations, purity levels, or distribution networks, this is your roadmap.
Understanding the Foundations of Drug Mixing
Before you dive into the lab, you need to internalize the basic principles that govern mixing. Schedule I doesn’t allow players to simply dump items together and produce results. Instead, it simulates chemical logic, meaning certain elements interact to create stronger effects, while others cancel each other out.

At the beginner stage, your focus should be on learning which base ingredients drive potency versus which ones only affect cost. For example, stimulants may increase short-term customer satisfaction but at the expense of higher side effect risks. On the other hand, stabilizers often dilute potency but extend shelf life, making your product more reliable to distribute.
Why Purity Matters
Purity determines both profit margin and risk. High-purity mixes attract wealthier clients but draw police attention faster. Low-purity blends move in larger quantities but create more dissatisfied users. Balancing purity is one of the first lessons new players must master.
The Role of Experimentation
Early on, don’t chase perfection. Treat every mixing session as a data-gathering opportunity. Keep written notes in-game or outside the game, because repeatable knowledge of ratios is your first weapon against randomness.
Gathering Ingredients Efficiently
Your mixes will only be as good as your supply chain. Unlike many crafting systems in other games, Schedule I makes the procurement of ingredients a challenge on its own. You can’t just buy everything outright—you must balance legality, cost, and accessibility.
The two main methods are street sourcing and bulk contracts. Street sourcing involves random encounters with dealers or smugglers who might offer rare components. This method is cheap but inconsistent. Bulk contracts, however, tie you to stable but expensive supplies.
Identifying Reliable Sources
Consistency matters more than raw luck. Many new players waste hours chasing rare spawns, when in reality, a stable bulk supplier—even at higher cost—lets you scale mixing operations without interruption.
Ingredient Storage
Storage is a subtle but critical part of ingredient management. Moisture, temperature, and time all degrade certain substances. Always invest in proper lab upgrades before stockpiling.
Building and Optimizing Your Lab
Once you have a consistent flow of ingredients, your lab becomes the backbone of your success. Schedule I’s lab system is modular—you can expand, upgrade, or reconfigure as you progress.
The most important aspect to consider is workflow efficiency. Players who clutter their space with poorly placed stations waste time switching between processes.
Core Equipment
At minimum, you’ll need:
- Mixing Station (base ratios)
- Purity Analyzer (testing batches)
- Heat Regulator (for volatile compounds)
- Storage Containers (preserving quality)
Workflow Design
Try designing your lab like a real assembly line: one end receives ingredients, the middle focuses on processing, and the other end packages the product. This not only saves time but reduces mistakes when handling multiple mixes simultaneously.
The Step-by-Step Mixing Process
Here’s where most players struggle. Mixing is not about luck—it’s about systematic testing.
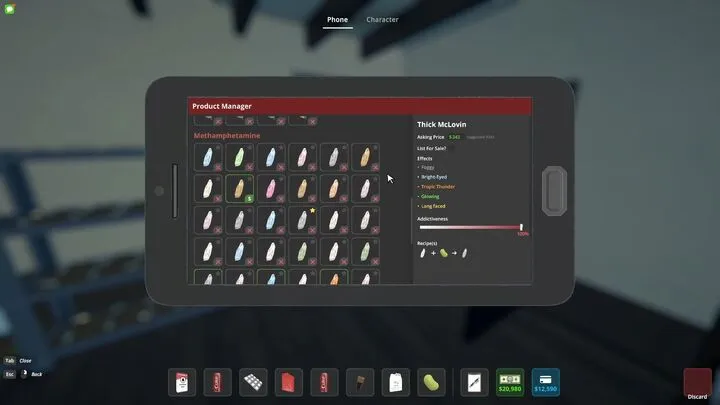
Step 1 – Choose Your Base
Every mix begins with a dominant base, which dictates the overall “feel” of the drug. Your choice here sets the tone: stimulant, depressant, hallucinogen, or hybrid.
Step 2 – Add Modifiers
Modifiers adjust potency, duration, or side effects. For example:
- Enhancers: Boost potency but increase addiction risk
- Stabilizers: Reduce volatility but lower high intensity
- Binders: Make pills easier to transport but increase bulk
Step 3 – Adjust Ratios
This is where trial-and-error becomes a science. Most successful players use 1:3:1 ratios early on and fine-tune based on feedback. Always document outcomes.
Testing and Calibrating Your Mix
Before distribution, you must test. Schedule I includes both lab testing and field testing.
Lab testing is safer but costly. It tells you purity, side effects, and estimated market demand. Field testing, however, means releasing small batches to trusted customers to gauge feedback.
Balancing Risk
Lab tests protect your reputation, but field tests help you adapt to evolving customer tastes. Combining both gives you the best information.
Long-Term Calibration
Don’t expect a formula to stay dominant forever. AI-driven market demand changes dynamically. You’ll need to adjust formulas over time to remain competitive.
Branding and Marketing Your Product
Mixing is only half the battle. To succeed in Schedule I, you must brand your drug like a real underground entrepreneur.

Branding involves naming, packaging, and reputation. A mix with strong branding can outsell a technically superior rival because customers crave consistency and identity.
Choosing a Name
Names should reflect either effect (“Night Pulse”) or exclusivity (“Golden Line”). Avoid generic terms that make your brand forgettable.
Packaging Strategy
Pills, powders, or liquid vials—each appeals to different demographics. For example, pills fit high-income clients, while powders dominate street sales.
Distribution Networks and Logistics
Once you have a branded mix, you must build distribution. Schedule I challenges you with logistics that mimic real-world underground trade.
Direct Street Sales
Profitable but risky, as they expose you to law enforcement. Best for early game small-batch selling.
Middlemen and Dealers
Using middlemen reduces risk but cuts profits. However, this is the only way to scale beyond small local networks.
Transport Security
Invest in safer vehicles and hidden compartments once you’re moving large shipments. Losing a batch to a police bust can set you back hours of progress.
Managing Risk and Avoiding Law Enforcement
The higher your success, the more heat you attract. Risk management becomes essential.
Heat Levels
Schedule I uses a “heat meter” to track law enforcement suspicion. Every bad batch, overdose, or loud marketing spike increases your heat.
Risk Mitigation
- Rotate distribution routes
- Frequently rebrand
- Pay off informants and police contacts
Staying one step ahead ensures longevity.
Scaling Into Advanced Operations
At this point, you’ve mastered small to medium batches. The next challenge is scaling operations while maintaining quality.
Scaling means more suppliers, bigger labs, and larger distribution chains. However, scale often dilutes control. You must set clear quality benchmarks and enforce them across all operations.

Automating Processes
Invest in lab assistants and automated testing equipment to keep output high without burning out.
Diversifying Products
Don’t rely on one formula. Markets shift. Keeping at least three variations ensures stability if one product loses popularity.
Becoming a Legendary Mixer
The final stage of mastery is reputation. In Schedule I, becoming a legend means players recognize your mixes as industry-defining.
The Reputation Loop
Reputation feeds demand, which increases profit, which funds better labs, which creates better mixes, which further grows reputation.
Staying on Top
Legends don’t just make great drugs—they adapt to every new trend, competitor, and crackdown. Never become complacent.
Conclusion
Mastering drug mixing in Schedule I is not about chasing one perfect formula. It’s about embracing a long-term cycle of experimentation, branding, distribution, and adaptation. Beginners should focus on understanding purity, ratios, and supply chains. Intermediates refine branding and logistics, while experts scale operations and defend their legacy against law enforcement pressure.
If you follow this guide step by step, you won’t just survive—you’ll dominate. Every choice you make in the lab echoes through the streets, shaping your reputation, profits, and legacy in Schedule I.

















